Introduction:
Prostate cancer is a prevalent disease that affects the prostate gland, which is an essential part of the male reproductive system. As a patient-centred healthcare provider, Nyaho Medical Centre believes it is crucial to educate everyone on prostate cancer, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By empowering ourselves with knowledge, we can make informed decisions about our health and work towards effective prevention and early detection strategies.
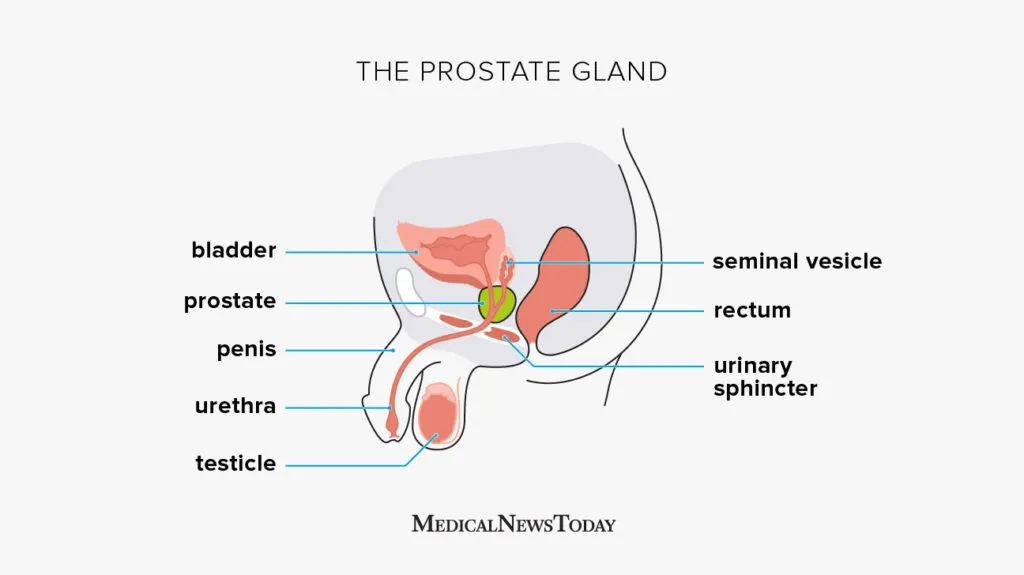
Understanding the Prostate and Its Functions
The prostate is a small walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It plays a vital role in the production of seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. As men age, the prostate gland may undergo changes, including the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown, but certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, particularly after the age of 50. The majority of prostate cancer cases occur in men over the age of 65.
- Family history: Having a close relative, such as a father or brother, with prostate cancer increases the risk. The risk is higher if the affected relative was diagnosed at a younger age.
- Race and ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to men of other racial or ethnic backgrounds. They also tend to have more aggressive forms of the disease.
- Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a high-fat diet, obesity, lack of exercise, and smoking, may contribute to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Recognizing the Symptoms
In the early stages, prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may manifest:
- Frequent urination, especially at night.
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination.
- Weak or interrupted urine flow.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Bone pain (if the cancer has spread to the bones).
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions unrelated to prostate cancer. Nevertheless, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Diagnosis and Screening
Early detection of prostate cancer greatly improves treatment outcomes. Various diagnostic tests and screening methods are available, including:
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: This blood test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate abnormalities, including cancer. However, PSA levels can also be elevated due to non-cancerous conditions, such as BPH.
- Digital rectal examination (DRE): In this physical examination, a healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to assess the size, shape, and texture of the prostate gland.
- Biopsy: If abnormalities are detected through the PSA test or DRE, a biopsy may be recommended. During a biopsy, a small sample of prostate tissue is collected and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage and intensity of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Treatment options for prostate cancer include:
- Active surveillance: For slow-growing tumours or when the patient’s age or health status makes immediate treatment unnecessary, active surveillance involves closely monitoring the cancer without active intervention.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the prostate gland, known as a prostatectomy, may be recommended. This can be done through open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy X-rays or other radiation sources are used to target and kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be delivered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
- Hormone therapy: Prostate cancer cells are often stimulated by male hormones (androgens), so hormone therapy is used to block or reduce the effects of androgens on cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. It is typically used in advanced cases or when cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Living with Prostate Cancer
Coping with prostate cancer involves more than just medical treatment. It is important to address the emotional and psychological impact of the disease. Seek support from loved ones, join support groups, and consider counselling or therapy to manage stress, anxiety, and any other emotional challenges you may face.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on your overall well-being. Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for monitoring and follow-up care.
Regular check-ups and ongoing communication with your healthcare team are essential for managing prostate cancer effectively. Remember, early detection and proactive management are key to improving outcomes and maintaining a good quality of life.
If you have any concerns or questions regarding prostate cancer or your health in general, consult our healthcare professionals, here at Nyaho Medical Centre for personalized advice and guidance.
